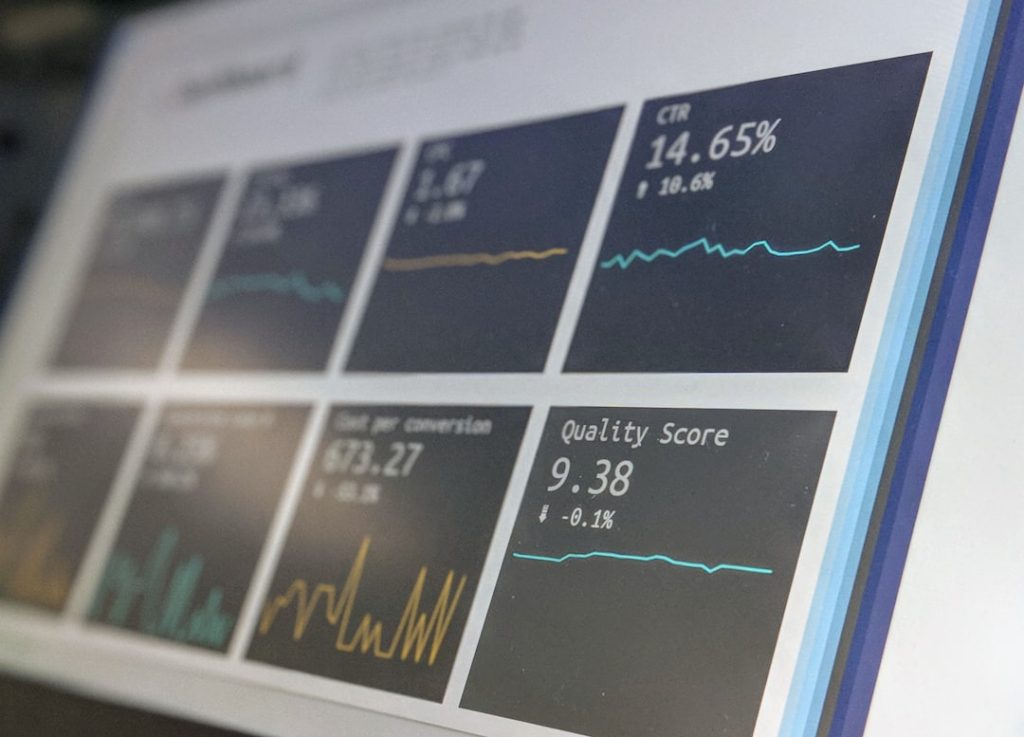
In the contemporary business landscape, the term “business analytics” has emerged as a cornerstone for organizations striving to gain a competitive edge. Business analytics refers to the systematic use of data, statistical analysis, and quantitative methods to drive decision-making and improve business performance. It encompasses a wide range of techniques, from descriptive analytics that summarize historical data to prescriptive analytics that recommend actions based on predictive models.
As companies increasingly recognize the value of data-driven insights, the demand for skilled professionals in this field has surged, leading to a proliferation of tools and methodologies designed to harness the power of data. The significance of business analytics extends beyond mere number-crunching; it is about transforming raw data into actionable insights that can inform strategic initiatives. Organizations that effectively leverage analytics can identify trends, uncover hidden patterns, and make informed predictions about future outcomes.
This capability not only enhances operational efficiency but also fosters innovation by enabling businesses to respond swiftly to market changes. As we delve deeper into the various facets of business analytics, it becomes evident that understanding data and metrics is foundational to unlocking its full potential.
Key Takeaways
- Business analytics involves the use of data and statistical methods to analyze and interpret business performance.
- Data and metrics are essential components of business analytics, providing valuable insights into customer behavior and market trends.
- Predictive analytics uses historical data to forecast future trends and outcomes, helping businesses make informed decisions.
- Business intelligence tools help businesses gather, store, and analyze data to gain actionable insights and improve decision-making.
- Customer insights are crucial for understanding and meeting customer needs, improving products and services, and driving business growth.
Understanding Data and Metrics
At the heart of business analytics lies the concept of data, which can be categorized into various types, including structured and unstructured data. Structured data refers to information that is organized in a predefined manner, such as databases and spreadsheets, making it easily searchable and analyzable. In contrast, unstructured data encompasses a vast array of formats, including text documents, social media posts, and multimedia content, which require more sophisticated techniques for extraction and analysis.
Understanding these distinctions is crucial for businesses aiming to implement effective analytics strategies, as it influences the choice of tools and methodologies employed in the analysis process. Metrics play a pivotal role in business analytics by providing quantifiable measures that can be tracked over time. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are specific metrics that organizations use to evaluate their success in achieving strategic objectives.
For instance, a retail company might track sales growth, customer acquisition costs, and inventory turnover as KPIs to assess its performance. By establishing clear metrics aligned with business goals, organizations can create a framework for continuous improvement. Furthermore, the ability to visualize these metrics through dashboards and reports enhances comprehension and facilitates communication across teams, ensuring that everyone is aligned toward common objectives.
Utilizing Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics represents a significant advancement in the field of business analytics, allowing organizations to forecast future trends based on historical data. By employing statistical algorithms and machine learning techniques, businesses can analyze past behaviors and identify patterns that may indicate future outcomes. For example, a financial institution might use predictive analytics to assess credit risk by analyzing customer transaction histories and demographic information.
This proactive approach not only aids in risk management but also enhances customer service by enabling personalized offerings tailored to individual preferences. The implementation of predictive analytics requires a robust data infrastructure and a commitment to continuous learning. Organizations must invest in data collection processes that ensure high-quality input for their predictive models.
Additionally, it is essential to foster a culture of experimentation where teams are encouraged to test hypotheses and refine their models based on real-world outcomes. As predictive analytics matures within an organization, it can lead to more informed decision-making across various functions, from marketing strategies to supply chain management. Ultimately, the ability to anticipate future trends empowers businesses to stay ahead of the competition and adapt swiftly to changing market dynamics.
Implementing Business Intelligence Tools
| Metrics | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of BI tools implemented | 5 |
| Percentage increase in data accuracy | 20% |
| Time saved on reporting processes | 30% |
| Number of users trained on BI tools | 50 |
The integration of business intelligence (BI) tools into an organization’s analytics strategy is crucial for transforming raw data into meaningful insights. BI tools encompass a range of software applications designed to analyze data and present actionable information through visualizations such as charts, graphs, and dashboards. These tools enable users at all levels of an organization to access relevant data without requiring extensive technical expertise.
By democratizing access to information, BI tools foster a data-driven culture where employees can make informed decisions based on real-time insights. Implementing BI tools involves careful consideration of several factors, including user needs, data sources, and integration capabilities with existing systems. Organizations must assess their specific requirements and choose tools that align with their strategic objectives.
Additionally, training employees on how to effectively utilize these tools is essential for maximizing their potential. As users become proficient in leveraging BI tools, they can uncover valuable insights that drive operational improvements and enhance customer experiences. The ongoing evolution of BI technology continues to expand its capabilities, making it an indispensable component of modern business analytics.
Leveraging Customer Insights
Customer insights are invaluable assets for any organization seeking to enhance its offerings and improve customer satisfaction. By analyzing customer behavior, preferences, and feedback through various channels—such as surveys, social media interactions, and purchase histories—businesses can gain a deeper understanding of their target audience. This knowledge enables organizations to tailor their products and services to meet customer needs more effectively, ultimately fostering loyalty and driving revenue growth.
Moreover, leveraging customer insights goes beyond mere analysis; it involves creating actionable strategies based on the findings. For instance, businesses can segment their customer base into distinct groups based on purchasing behavior or demographics, allowing for targeted marketing campaigns that resonate with specific audiences. Additionally, organizations can utilize sentiment analysis tools to gauge customer opinions about their brand or products in real-time.
By continuously monitoring customer feedback and adapting strategies accordingly, companies can maintain a competitive edge in an ever-evolving marketplace.
Optimizing Operations with Analytics
Operational efficiency is a critical determinant of success in today’s fast-paced business environment. By employing analytics to optimize operations, organizations can identify bottlenecks, streamline processes, and reduce costs. For example, manufacturers can utilize predictive maintenance analytics to anticipate equipment failures before they occur, minimizing downtime and extending the lifespan of machinery.
Similarly, supply chain analytics can provide insights into inventory levels and demand forecasting, enabling businesses to maintain optimal stock levels while reducing excess inventory costs. The optimization process often involves cross-functional collaboration among various departments within an organization. By breaking down silos and fostering communication between teams such as operations, finance, and marketing, businesses can create a holistic view of their operations.
This collaborative approach allows for more informed decision-making based on comprehensive data analysis rather than isolated departmental metrics. As organizations embrace a culture of continuous improvement driven by analytics, they position themselves for long-term success in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Making Strategic Decisions with Data
Data-driven decision-making has become a hallmark of successful organizations across industries. By grounding strategic decisions in empirical evidence rather than intuition or anecdotal experiences, businesses can mitigate risks and enhance their chances of success. For instance, when launching a new product line, companies can analyze market trends and consumer preferences through data analytics to determine optimal pricing strategies and marketing approaches.
This reliance on data not only increases confidence in decision-making but also fosters accountability within teams. Furthermore, the integration of advanced analytics into strategic planning processes allows organizations to simulate various scenarios and assess potential outcomes before committing resources. This capability enables leaders to explore different strategies based on varying assumptions about market conditions or competitive actions.
As organizations become more adept at utilizing data for strategic decision-making, they cultivate an agile mindset that empowers them to pivot quickly in response to changing circumstances or emerging opportunities.
Measuring and Monitoring Performance
The final piece of the business analytics puzzle involves measuring and monitoring performance through established metrics and KPIs. Continuous performance measurement is essential for assessing progress toward strategic goals and identifying areas for improvement. Organizations must establish a framework for regular performance reviews that includes both quantitative metrics—such as sales figures or customer retention rates—and qualitative assessments—such as employee satisfaction or brand perception.
Moreover, leveraging technology plays a crucial role in performance monitoring by automating data collection and reporting processes. Business intelligence dashboards can provide real-time insights into key metrics, allowing leaders to make timely adjustments as needed. By fostering a culture of accountability where teams are encouraged to track their performance against established benchmarks, organizations can drive continuous improvement efforts that align with their overall strategic objectives.
Ultimately, effective measurement and monitoring not only enhance operational efficiency but also contribute to sustained organizational growth in an increasingly complex business environment.
If you’re interested in learning more about the team behind the insightful business analytics content, consider visiting their “About Us” page. This page provides detailed information about the expertise and background of the contributors who analyze complex data to deliver actionable business insights. You can access this information by clicking on the following link: