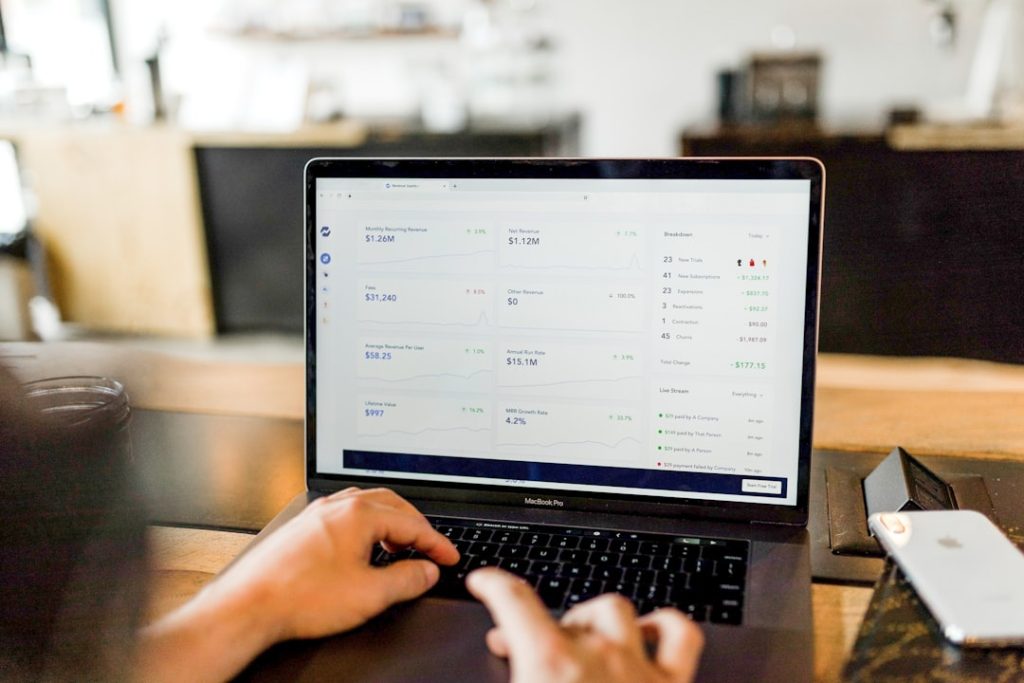
Online Analytical Processing, commonly referred to as OLAP, is a powerful technology that enables users to perform multidimensional analysis of business data. At its core, OLAP allows for the quick retrieval and analysis of large volumes of data, facilitating complex calculations, trend analysis, and sophisticated data modeling. The architecture of OLAP is designed to support decision-making processes by providing a framework that allows users to view data from various perspectives.
This multidimensional approach is often visualized as a cube, where each dimension represents a different aspect of the data, such as time, geography, or product categories. By slicing and dicing this cube, users can drill down into specific data points or roll up to see aggregated information, making it an invaluable tool for businesses seeking to derive actionable insights from their data. The significance of OLAP extends beyond mere data retrieval; it encompasses the ability to perform advanced analytical operations that are essential for strategic planning and operational efficiency.
OLAP systems are typically categorized into two main types: MOLAP (Multidimensional OLAP) and ROLAP (Relational OLAP). MOLAP stores data in a multidimensional cube format, which allows for rapid query performance and efficient storage of aggregated data. In contrast, ROLAP leverages relational databases to store data, providing flexibility in handling large datasets but often at the cost of slower query performance.
Regardless of the type, OLAP systems are designed to support complex queries that can involve multiple dimensions and hierarchies, enabling businesses to analyze their data in a way that is both intuitive and insightful.
Key Takeaways
- OLAP is a technology that allows users to analyze multidimensional data from different perspectives, providing faster and more interactive access to data for business insights.
- Businesses can leverage OLAP to gain insights into sales trends, customer behavior, and market analysis, enabling better decision-making and strategic planning.
- Implementing OLAP tools and technologies involves selecting the right software, designing efficient data models, and optimizing query performance for effective data analysis.
- OLAP can be utilized for data visualization and reporting, enabling users to create interactive dashboards and reports for better communication of insights.
- Integrating OLAP with business intelligence systems allows for seamless access to OLAP data within existing BI platforms, enhancing overall data analysis capabilities.
Leveraging OLAP for Business Insights
The ability to leverage OLAP for business insights is one of its most compelling features. Organizations can utilize OLAP tools to uncover trends and patterns that may not be immediately apparent through traditional reporting methods. For instance, by analyzing sales data across different regions and time periods, businesses can identify seasonal trends or regional preferences that inform marketing strategies and inventory management.
This level of insight allows companies to make data-driven decisions that enhance operational efficiency and improve customer satisfaction. Furthermore, OLAP enables users to conduct “what-if” analyses, allowing them to simulate various scenarios and assess potential outcomes based on different variables. This capability is particularly valuable in strategic planning, where understanding the implications of various decisions can lead to more informed choices.
Moreover, OLAP empowers users at all levels of an organization to engage with data in a meaningful way. With user-friendly interfaces and intuitive visualization tools, even non-technical users can explore complex datasets without needing extensive training in data analysis. This democratization of data access fosters a culture of analytics within organizations, encouraging employees to rely on data for decision-making rather than intuition alone.
As a result, businesses can become more agile and responsive to market changes, as they are equipped with the insights necessary to adapt quickly. By integrating OLAP into their analytical processes, organizations can not only enhance their understanding of current performance but also anticipate future trends and challenges.
Implementing OLAP Tools and Technologies
Implementing OLAP tools and technologies requires careful planning and consideration of various factors that can influence the success of the deployment. One of the first steps in this process is assessing the specific analytical needs of the organization. Different industries may have unique requirements when it comes to data analysis, so understanding these needs is crucial for selecting the right OLAP solution.
Organizations must evaluate their existing data infrastructure, including the types of databases they use and the volume of data they need to analyze. This assessment will help determine whether a MOLAP or ROLAP solution is more appropriate based on factors such as performance requirements and scalability. Once the appropriate OLAP technology has been selected, organizations must focus on data integration and preparation.
This involves consolidating data from various sources into a unified format that can be easily analyzed within the OLAP environment. Data cleansing and transformation are critical steps in this process, as they ensure that the information being analyzed is accurate and relevant. Additionally, organizations should consider establishing a governance framework to manage data quality and security throughout the OLAP implementation.
By prioritizing these foundational elements, businesses can create a robust analytical environment that maximizes the value derived from their OLAP investments.
Utilizing OLAP for Data Visualization and Reporting
| Metrics | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of OLAP cubes created | 20 | 25 | 30 |
| Percentage of data visualization improvement | 15% | 20% | 25% |
| Number of reports generated | 100 | 120 | 150 |
Data visualization is an essential component of effective reporting, and OLAP plays a pivotal role in enhancing this aspect of business intelligence. By transforming complex datasets into visually appealing charts, graphs, and dashboards, OLAP tools enable users to quickly grasp key insights and trends without getting lost in raw numbers. The multidimensional nature of OLAP allows for dynamic visualizations that can be manipulated in real-time, providing users with the ability to explore different dimensions of their data interactively.
For example, a sales manager might use an OLAP dashboard to visualize sales performance by region while simultaneously filtering by product category or time period, allowing for a comprehensive view of business performance. Furthermore, the integration of OLAP with modern visualization tools enhances reporting capabilities significantly. Many organizations are now leveraging advanced analytics platforms that incorporate OLAP functionality alongside powerful visualization features.
This combination allows users to create customized reports that cater to specific business needs while ensuring that insights are presented in an easily digestible format. The ability to share these visual reports across teams fosters collaboration and encourages data-driven discussions within organizations. As businesses increasingly recognize the importance of storytelling through data, utilizing OLAP for visualization becomes a critical strategy for communicating insights effectively.
Integrating OLAP with Business Intelligence Systems
The integration of OLAP with broader business intelligence (BI) systems is essential for creating a cohesive analytical environment that supports informed decision-making across an organization. By connecting OLAP tools with other BI components such as data warehouses, reporting tools, and predictive analytics platforms, organizations can create a seamless flow of information that enhances overall analytical capabilities. This integration allows for a more comprehensive view of business performance by combining historical data analysis with real-time insights from various operational systems.
As a result, decision-makers can access a holistic understanding of their organization’s performance metrics. Moreover, integrating OLAP with BI systems facilitates advanced analytics capabilities such as predictive modeling and machine learning. By leveraging historical data stored within OLAP cubes alongside external datasets, organizations can develop sophisticated models that forecast future trends or identify potential risks.
This predictive capability empowers businesses to proactively address challenges before they escalate, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and competitive advantage. As organizations continue to embrace digital transformation initiatives, the integration of OLAP with BI systems will play a crucial role in driving innovation and enhancing overall business performance.
Best Practices for Analyzing Data with OLAP

To maximize the effectiveness of OLAP in analyzing data, organizations should adhere to several best practices that enhance both the quality of insights generated and the efficiency of the analytical process. One key practice is ensuring that data is well-structured and organized before it enters the OLAP environment. This involves implementing robust data governance policies that dictate how data is collected, stored, and maintained across the organization.
By establishing clear standards for data quality and consistency, businesses can reduce errors and discrepancies that may hinder accurate analysis within OLAP systems. Another important best practice is fostering a culture of collaboration among stakeholders involved in the analytical process. Encouraging cross-functional teams to work together on data analysis initiatives can lead to richer insights and more comprehensive understanding of business challenges.
Additionally, providing training and resources for employees at all levels ensures that they are equipped with the skills necessary to leverage OLAP tools effectively. By investing in user education and promoting collaboration, organizations can create an environment where data-driven decision-making thrives.
Overcoming Challenges in OLAP Implementation
Despite its many advantages, implementing OLAP systems can present several challenges that organizations must navigate effectively. One common hurdle is resistance to change among employees who may be accustomed to traditional reporting methods or hesitant to adopt new technologies. To address this challenge, organizations should prioritize change management strategies that emphasize the benefits of OLAP while providing adequate training and support for users during the transition period.
Engaging employees early in the implementation process can also help alleviate concerns and foster buy-in from key stakeholders. Another significant challenge lies in ensuring data quality and consistency across various sources before integrating them into an OLAP system. Inconsistent or inaccurate data can lead to misleading insights and undermine confidence in analytical results.
To mitigate this risk, organizations should establish rigorous data validation processes that identify discrepancies before they enter the OLAP environment. Additionally, ongoing monitoring of data quality post-implementation is essential for maintaining trust in analytical outputs over time. By proactively addressing these challenges, organizations can enhance their chances of successful OLAP implementation.
Future Trends in OLAP for Business Analytics
As technology continues to evolve at a rapid pace, several trends are emerging that will shape the future of OLAP in business analytics. One notable trend is the increasing adoption of cloud-based OLAP solutions, which offer greater scalability and flexibility compared to traditional on-premises systems. Cloud-based platforms enable organizations to access powerful analytical capabilities without the need for extensive infrastructure investments while also facilitating collaboration among geographically dispersed teams.
This shift towards cloud computing is likely to accelerate as businesses seek more agile solutions that can adapt to changing market conditions. Additionally, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are poised to enhance the capabilities of OLAP systems significantly. By integrating AI algorithms into OLAP processes, organizations can automate complex analyses and uncover deeper insights from their data more efficiently than ever before.
Predictive analytics powered by machine learning will enable businesses to anticipate trends and make proactive decisions based on real-time information rather than relying solely on historical patterns. As these technologies continue to mature, they will undoubtedly transform how organizations leverage OLAP for business analytics, paving the way for more sophisticated decision-making processes in the future.
For those interested in understanding more about how their data is managed during online analytical processing, it’s crucial to be aware of the privacy practices of the platforms you use. A good starting point is to review the privacy policy of the website in question. For instance, you can learn about how your personal information is handled by visiting XOSAP’s Privacy Policy. This document provides detailed information on what data is collected, how it is used, and the measures in place to protect your privacy while you engage with their services.
FAQs
What is online analytical processing (OLAP)?
Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) is a technology that enables analysts, managers, and executives to gain insight into data through fast, consistent, and interactive access to a wide variety of possible views of information.
How does OLAP differ from online transaction processing (OLTP)?
OLAP is designed for complex queries and analysis of data, while OLTP is designed for transaction-oriented applications, such as order entry and customer relationship management.
What are the main types of OLAP systems?
The main types of OLAP systems are Multidimensional OLAP (MOLAP), Relational OLAP (ROLAP), Hybrid OLAP (HOLAP), and In-Memory OLAP (IOLAP).
What are the benefits of using OLAP?
Some benefits of using OLAP include faster query performance, the ability to analyze large volumes of data, support for complex analytical queries, and the ability to create interactive reports and dashboards.
What are some common use cases for OLAP?
Common use cases for OLAP include financial reporting and analysis, sales and marketing analysis, inventory management, budgeting and forecasting, and customer relationship management analysis.
